reading-notes
Reading and Writing Files in Python
- What Is a File?
- a file is and how modern operating systems handle some of their aspects.
- a file is a contiguous set of bytes used to store data.
-
This data is organized in a specific format and can be anything as simple as a text file or as complicated as a program executable.
- Files on most modern file systems are composed of three main parts:
- Header: metadata about the contents of the file (file name, size, type, and so on)
- Data: contents of the file as written by the creator or editor
- End of file (EOF): special character that indicates the end of the file
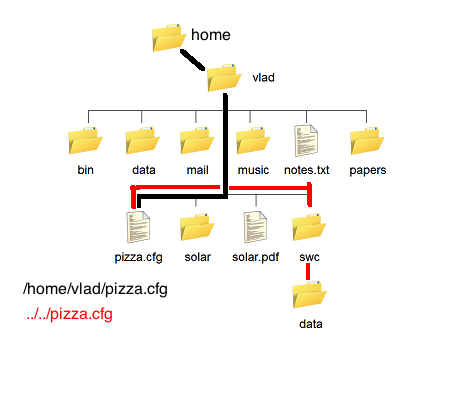
File Paths
- When you access a file on an operating system, a file path is required. The file path is a string that represents the location of a file.
-
- Folder Path: the file folder location on the file system where subsequent folders are separated by a forward slash,Unix ,Windows
-
- File Name: the actual name of the file
-
- Extension: the end of the file path pre-pended with a period (.) used to indicate the file type
- example:
- Tree of Files
│
├── path/
| │
│ ├── to/
│ │ └── cats.gif
│ │
│ └── dog_breeds.txt
|
└── animals.csv
Opening and Closing a File in Python
- When you want to work with a file, the first thing to do is to open it. This is done by invoking the open() built-in function. open() has a single required argument that is the path to the file.
- open() has a single return, the file object (Text files, Buffered binary files, Raw binary files).
About Python Exceptions
-
Syntax errors occur when the parser detects an incorrect statement. Observe the following example:
-
Example
>>> print( 0 / 0 ))
File "<stdin>", line 1
print( 0 / 0 ))
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
Raising an Exception
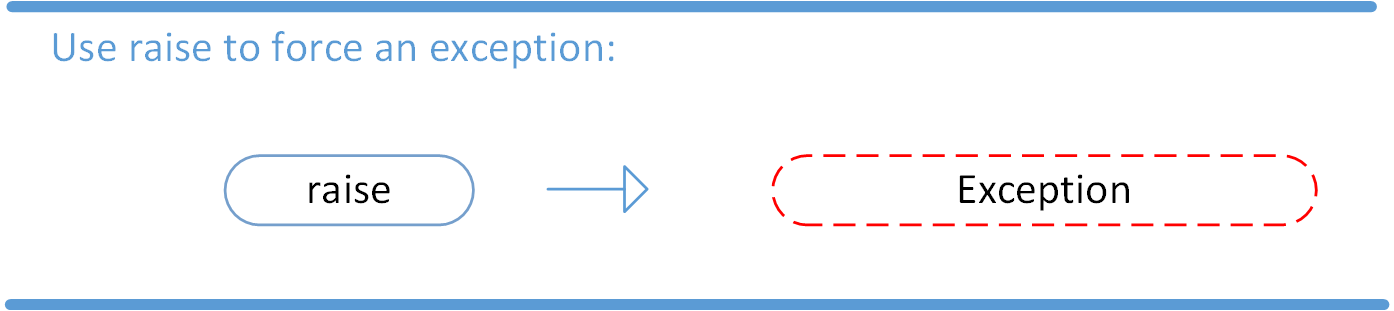
- We can use raise to throw an exception if a condition occurs. The statement can be complemented with a custom exception.
- Example image:
The AssertionError Exception
Instead of waiting for a program to crash midway, you can also start by making an assertion in Python. We assert that a certain condition is met. If this condition turns out to be True, then that is excellent! The program can continue. If the condition turns out to be False, you can have the program throw an AssertionError exception.
The else Clause
In Python, using the else statement, you can instruct a program to execute a certain block of code only in the absence of exceptions.
Usefull Content:
-
- raise allows you to throw an exception at any time.
-
- assert enables you to verify if a certain condition is met and throw an exception if it isn’t.
-
- In the try clause, all statements are executed until an exception is encountered.